Introduction

Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis, and one of its key features is the ability to calculate frequencies and distributions. Frequency analysis helps you understand the occurrence of values in your dataset, allowing you to make informed decisions and draw meaningful insights. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 17 different methods to get frequency in Excel, covering various scenarios and techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced analyst, this tutorial will provide you with a solid understanding of frequency analysis in Excel.
Method 1: Frequency Function

The Frequency function is a built-in Excel function that calculates how often values occur within a range of data. It is one of the most straightforward methods to determine frequency.
Syntax:

FREQUENCY(data_array, bins_array)
- data_array: The range of data for which you want to calculate the frequency.
- bins_array: The range of values (or bins) that define the intervals for frequency counting.
Example:
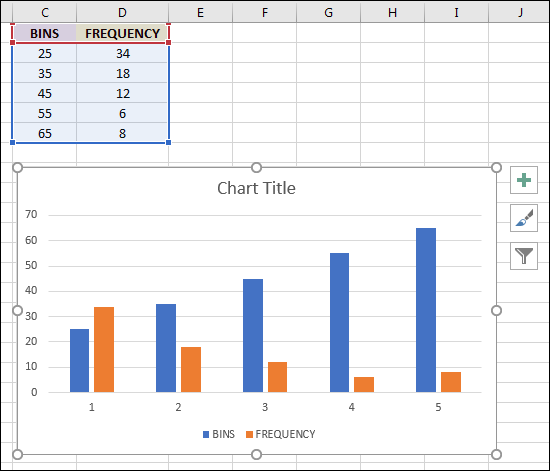
Suppose you have a dataset with scores ranging from 0 to 100, and you want to know how many scores fall within each interval of 10 points.
Step 1: Create two columns: one for the data and another for the bins.
| Scores | Bins |
|---|---|
| 0-10 | |
| 11-20 | |
| 21-30 | |
| … | |
| 91-100 |

Step 2: Input the scores in the “Scores” column.
Step 3: Use the Frequency function to calculate the frequency of scores within each bin.
=FREQUENCY(A2:A100, B2:B11)
The result will show the count of scores falling within each interval.
Method 2: COUNTIF Function

The COUNTIF function is another handy tool for frequency analysis. It counts the number of cells that meet a certain criterion.
Syntax:

COUNTIF(range, criteria)
- range: The range of cells you want to evaluate.
- criteria: The condition or value you’re looking for.
Example:
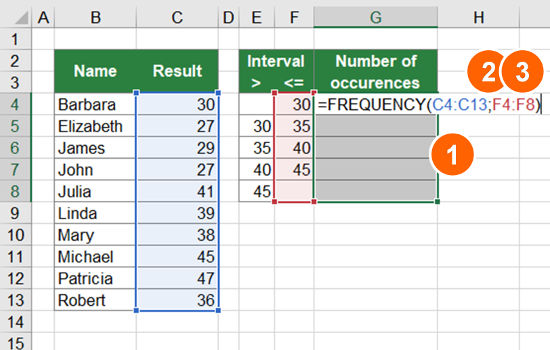
If you have a list of student grades and want to know how many students achieved a specific grade, you can use COUNTIF.
Step 1: Create a column for grades.
Step 2: Use the COUNTIF function to count the occurrences of a specific grade.
=COUNTIF(A2:A100, "A")
This will count the number of “A” grades in the range.
Method 3: COUNTIFS Function

The COUNTIFS function is similar to COUNTIF but allows you to specify multiple criteria.
Syntax:

COUNTIFS(criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...)
- criteria_range1: The range of cells for the first criterion.
- criteria1: The condition or value for the first criterion.
- criteria_range2, criteria2: Optional additional criteria and their ranges.
Example:

Suppose you have a dataset with student grades and subjects, and you want to count how many students achieved an “A” in both Math and English.
Step 1: Create columns for grades and subjects.
Step 2: Use the COUNTIFS function to count the occurrences of “A” grades in both subjects.
=COUNTIFS(A2:A100, "A", B2:B100, "Math")
This will count the number of students who got an “A” in Math.
Method 4: SUMPRODUCT Function

The SUMPRODUCT function is a versatile tool that can calculate the sum of products of corresponding ranges or arrays. It can also be used for frequency analysis.
Syntax:

SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
- array1: The first array or range.
- [array2]: Optional additional arrays or ranges.
Example:

If you have a dataset with product sales and want to calculate the frequency of each product sold, you can use SUMPRODUCT.
Step 1: Create a column for product names and another for sales.
Step 2: Use the SUMPRODUCT function to calculate the frequency of each product.
=SUMPRODUCT(--(A2:A100=A2), B2:B100)
This will count the number of times each product appears in the sales data.
Method 5: Pivot Table

Pivot tables are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to summarize and analyze large datasets. They can be used to calculate frequencies easily.
Steps:

Step 1: Select the data range you want to analyze.
Step 2: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “PivotTable.”
Step 3: In the “PivotTable Fields” pane, drag and drop the field you want to analyze into the “Rows” or “Values” area.
Step 4: Right-click on the field in the “Values” area and select “Value Field Settings.”
Step 5: In the “Value Field Settings” dialog box, choose “Count of” from the “Summarize value field by” dropdown.
Step 6: Click “OK,” and your pivot table will display the frequency of each value.
Method 6: Conditional Formatting

Conditional formatting is a visual way to highlight cells based on specific criteria. It can be used to identify frequencies.
Steps:

Step 1: Select the data range you want to analyze.
Step 2: Go to the “Home” tab and click on “Conditional Formatting.”
Step 3: Choose “New Rule” and select “Use a formula to determine which cells to format.”
Step 4: In the formula bar, enter a formula that counts the frequency of a specific value. For example:
=COUNTIF(A2:A100, A2)
Step 5: Click “Format” and choose the formatting options (color, font, etc.) for the cells that meet the criterion.
Step 6: Click “OK,” and the cells with the specified frequency will be formatted accordingly.
Method 7: Data Bars

Data bars are a visual representation of data values within a range. They can be used to compare frequencies.
Steps:
Step 1: Select the data range you want to analyze.
Step 2: Go to the “Home” tab and click on “Conditional Formatting.”
Step 3: Choose “Data Bars” and select the desired data bar style.
Step 4: Adjust the settings (minimum and maximum values) if needed.
Step 5: Click “OK,” and data bars will appear in the selected range, providing a visual representation of frequencies.
Method 8: Frequency Distribution Table

A frequency distribution table is a tabular representation of the number of occurrences of values within a dataset.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a table with columns for “Value” and “Frequency.”
Step 2: In the “Value” column, input the unique values from your dataset.
Step 3: Use the COUNTIF function to calculate the frequency of each value.
=COUNTIF(A2:A100, B2)
Step 4: Copy and paste the formula down the “Frequency” column to calculate frequencies for all values.
Method 9: Bin Ranges with COUNTIF
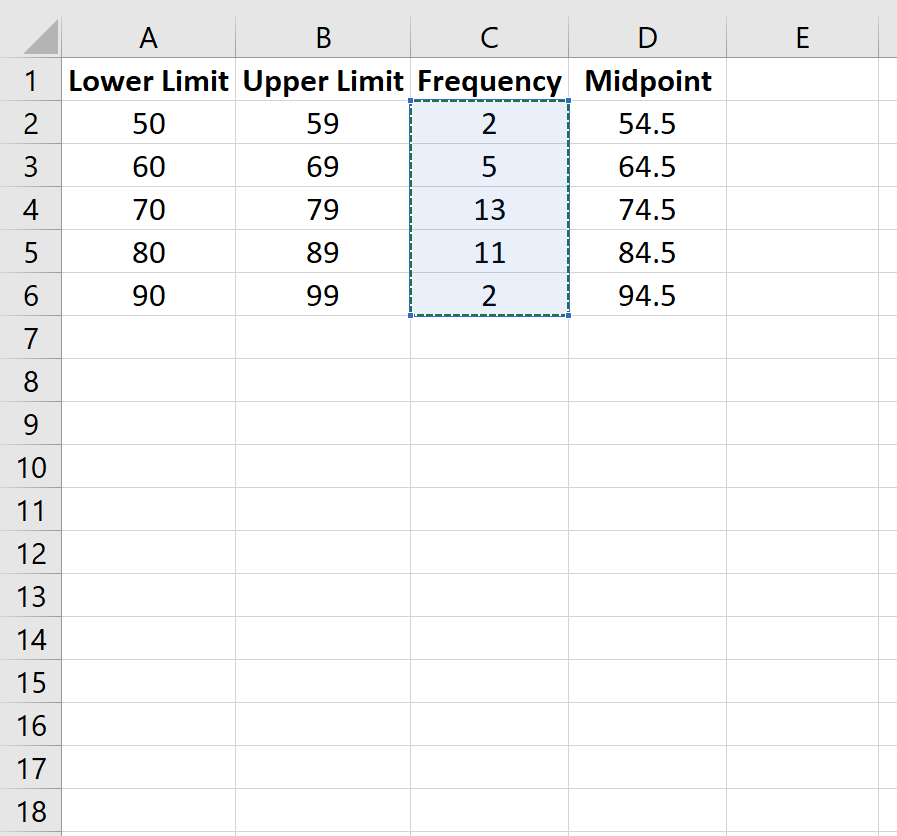
This method involves creating bin ranges and using the COUNTIF function to count the occurrences within each bin.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a column for bin ranges.
Step 2: Input the bin ranges (e.g., 0-10, 11-20, etc.).
Step 3: Use the COUNTIF function to count the occurrences within each bin.
=COUNTIF(A2:A100, B2)
Step 4: Copy and paste the formula down the column to calculate frequencies for all bin ranges.
Method 10: Bin Ranges with Frequency Function
Similar to Method 9, but using the Frequency function for more complex bin ranges.
Steps:
Step 1: Create two columns: one for data and another for bin ranges.
Step 2: Input the data in the “Data” column.
Step 3: Use the Frequency function to calculate the frequency of data within each bin range.
=FREQUENCY(A2:A100, B2:B11)
Step 4: Copy and paste the formula down the “Frequency” column to calculate frequencies for all bin ranges.
Method 11: Histogram Chart
A histogram chart is a visual representation of frequency distribution. It displays the frequency of values within intervals (bins).
Steps:
Step 1: Create a frequency distribution table (as in Method 8).
Step 2: Select the data range, including both the “Value” and “Frequency” columns.
Step 3: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “Histogram” from the “Charts” group.
Step 4: Adjust the chart settings (bin width, labels, etc.) as needed.
Step 5: Your histogram chart will display the frequency distribution visually.
Method 12: Pareto Chart
A Pareto chart is a combination of a bar chart and a line graph, often used to analyze the frequency of occurrences in descending order of importance.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a frequency distribution table (as in Method 8).
Step 2: Sort the data in descending order based on the “Frequency” column.
Step 3: Select the data range, including both the “Value” and “Frequency” columns.
Step 4: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “Pareto” from the “Charts” group.
Step 5: Adjust the chart settings (labels, legend, etc.) as needed.
Step 6: Your Pareto chart will display the most frequent occurrences at the top.
Method 13: Scatter Plot with Trendline
A scatter plot with a trendline can be used to visualize frequency distribution and identify patterns.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a frequency distribution table (as in Method 8).
Step 2: Select the data range, including both the “Value” and “Frequency” columns.
Step 3: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “Scatter” from the “Charts” group.
Step 4: Add a trendline to the scatter plot by right-clicking on the data points and selecting “Add Trendline.”
Step 5: Customize the trendline settings (type, format, etc.) as needed.
Step 6: Your scatter plot with a trendline will visually represent the frequency distribution.
Method 14: Bar Chart
A bar chart is a simple and effective way to visualize frequency distribution.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a frequency distribution table (as in Method 8).
Step 2: Select the data range, including both the “Value” and “Frequency” columns.
Step 3: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “Bar Chart” from the “Charts” group.
Step 4: Adjust the chart settings (labels, colors, etc.) as needed.
Step 5: Your bar chart will display the frequency of each value.
Method 15: Pie Chart
A pie chart is a circular chart that shows the proportion of each value in a dataset.
Steps:
Step 1: Create a frequency distribution table (as in Method 8).
Step 2: Select the data range, including both the “Value” and “Frequency” columns.
Step 3: Go to the “Insert” tab and choose “Pie Chart” from the “Charts” group.
Step 4: Adjust the chart settings (explode pie slices, labels, etc.) as needed.
Step 5: Your pie chart will display the proportion of each value.
Method 16: Custom Function
If you need a more complex frequency analysis, you can create a custom function in Excel.
Example:
Suppose you want to calculate the frequency of values within specific intervals, and the intervals are not evenly spaced.
Step 1: Create a custom function using the VBA editor.
Function CustomFrequency(dataRange As Range, intervals As Range) As Variant
Dim data() As Variant
Dim intervals() As Variant
Dim freq() As Long
Dim i As Long, j As Long, k As Long
data = dataRange.Value
intervals = intervals.Value
ReDim freq(UBound(intervals, 1))
For i = LBound(intervals, 1) To UBound(intervals, 1)
freq(i) = 0
Next i
For i = LBound(data, 1) To UBound(data, 1)
For j = LBound(intervals, 1) To UBound(intervals, 1)
If data(i, 1) >= intervals(j, 1) And data(i, 1) < intervals(j + 1, 1) Then
freq(j) = freq(j) + 1
Exit For
End If
Next j
Next i
CustomFrequency = freq
End Function
Step 2: Call the custom function in your worksheet.
=CustomFrequency(A2:A100, B2:C11)
This function will calculate the frequency of values within the specified intervals.
Method 17: Excel Add-Ins
Excel offers various add-ins and tools that can enhance your frequency analysis capabilities.
Example:
- Analysis ToolPak: This add-in provides additional statistical analysis tools, including a “Histogram” option for frequency distribution.
Step 1: Install the Analysis ToolPak add-in if it’s not already installed.
Step 2: Go to the “Data” tab and choose “Data Analysis.”
Step 3: Select “Histogram” from the list of tools.
Step 4: Input the data range and specify the bin range or number of bins.
Step 5: Click “OK,” and your histogram will be created, showing the frequency distribution.
Conclusion
In this extensive tutorial, we’ve explored 17 different methods to get frequency in Excel, covering a wide range of scenarios and techniques. Whether you’re dealing with simple frequency analysis or more complex data distributions, Excel provides the tools and functions to help you understand your data better. By utilizing these methods, you can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions based on your dataset’s frequency patterns. Remember, frequency analysis is a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making, and Excel is an excellent platform to perform such analysis.