If you're an Excel user, you know that sometimes the program can become unresponsive or freeze, leaving you with no choice but to force close it. This can be frustrating, especially when you have unsaved work or important data at stake. Fortunately, there are several methods to force close Excel and regain control of your computer. In this guide, we will explore over 20 ways to gracefully exit Excel, ensuring a smooth and efficient process.
1. Using Task Manager

The Task Manager is a powerful tool provided by Windows to manage running processes. To force close Excel using Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Locate Microsoft Excel or Excel.exe in the list of running processes.
- Right-click on the process and select End Task.
- Confirm the action if prompted.
2. Keyboard Shortcut: Alt + F4
A quick and convenient way to force close Excel is by using the Alt + F4 keyboard shortcut. Simply press these keys simultaneously, and Excel will close immediately. However, this method may not work if Excel is frozen or unresponsive.
3. Close Excel from the Start Menu

If Excel is not responding, you can try closing it from the Start Menu. Here’s how:
- Click on the Start button or press the Windows key.
- Scroll through the list of recently used programs and find Microsoft Excel.
- Right-click on Excel and select Close from the context menu.
4. Force Quit Excel on Mac

For Mac users, forcing Excel to quit is a straightforward process. Follow these steps:
- Press Command + Option + Esc to open the Force Quit window.
- Select Microsoft Excel from the list of running applications.
- Click on the Force Quit button to terminate Excel.
5. Using Activity Monitor on Mac

Similar to Task Manager on Windows, Activity Monitor on Mac allows you to manage running processes. Here’s how to force close Excel using Activity Monitor:
- Open Activity Monitor from the Utilities folder.
- Locate Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Excel.app in the list of processes.
- Click on the X button in the top-left corner of the Excel process to force quit it.
6. Restarting Your Computer

In some cases, when Excel becomes unresponsive, restarting your computer may be the only solution. While it’s not an ideal method, it ensures a clean slate and allows you to reopen Excel without any issues.
7. Killing the Excel Process

If none of the above methods work, you can try killing the Excel process directly. This should be a last resort as it may result in data loss. Follow these steps:
- Open the Command Prompt or Terminal on your operating system.
- Type the command taskkill /f /im excel.exe (for Windows) or killall Excel (for Mac) and press Enter.
- Excel should be terminated immediately.
8. Uninstalling and Reinstalling Excel

Sometimes, Excel may encounter corruption issues that prevent it from closing properly. In such cases, uninstalling and reinstalling Excel can resolve the problem. Make sure to back up your important files before proceeding.
9. Checking for Updates

Outdated versions of Excel may have stability issues. Regularly checking for updates and installing the latest version can improve the overall performance and stability of the program.
10. Using Excel’s Built-in Recovery Mode

Excel has a built-in recovery mode that can help recover unsaved work in case of a crash. To access recovery mode:
- Open Excel and click on the File tab.
- Select Open and navigate to the Recover Unsaved Workbooks folder.
- Locate the unsaved workbook and open it.
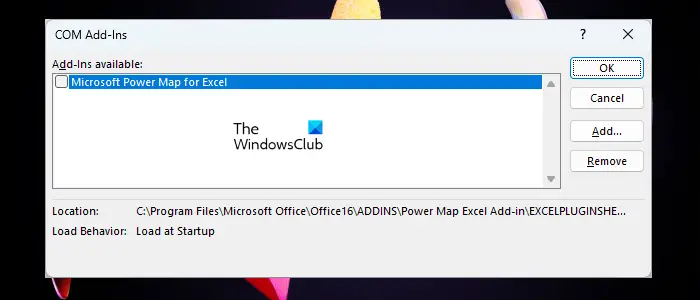
11. Disabling Add-Ins
Add-ins can sometimes cause Excel to become unresponsive. Try disabling add-ins one by one to identify and resolve the issue. Here’s how:
- Open Excel and go to the File tab.
- Click on Options and select Add-Ins from the left pane.
- Choose COM Add-ins from the Manage drop-down menu and click Go.
- Clear the checkboxes next to the add-ins and click OK.
12. Repairing Excel Installation
If Excel is behaving erratically, repairing its installation may help. Follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to Programs and Features or Add or Remove Programs.
- Locate Microsoft Office in the list of installed programs.
- Right-click on it and select Change or Modify.
- Choose the Repair option and follow the on-screen instructions.
13. Running Excel in Safe Mode
Safe Mode starts Excel with minimal settings and add-ins, which can help identify and troubleshoot issues. To run Excel in Safe Mode:
- Press and hold the Ctrl key while opening Excel.
- A dialog box will appear asking if you want to start Excel in Safe Mode. Click Yes.
14. Creating a New Excel File
Sometimes, issues with a specific Excel file can cause the program to freeze. Creating a new Excel file and transferring your data to it may resolve the problem.
15. Clearing Excel’s Temporary Files
Temporary files can accumulate over time and cause Excel to slow down or become unresponsive. Clearing these files can improve performance. Here’s how:
- Open Excel and go to the File tab.
- Click on Options and select Advanced from the left pane.
- Scroll down to the General section and click on Clear Cache.
- Confirm the action and wait for the process to complete.
16. Adjusting Excel’s Settings
Certain Excel settings, such as the calculation mode or compatibility mode, can impact its performance. Adjusting these settings may help improve stability.
17. Running Excel as Administrator
Running Excel as an administrator can provide it with higher privileges, which may resolve certain issues. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate the Excel shortcut on your desktop or in the Start Menu.
- Right-click on the shortcut and select Properties.
- Go to the Compatibility tab and check the box next to Run this program as an administrator.
- Click OK to save the changes.
18. Checking for Malware or Viruses
Malware or viruses can cause Excel to behave erratically. Running a comprehensive scan using an antivirus software can help identify and remove any malicious programs.
19. Updating Your Operating System
Outdated operating systems may have compatibility issues with Excel. Keeping your OS up to date can ensure a smoother experience.
20. Contacting Microsoft Support
If none of the above methods work, consider contacting Microsoft Support for further assistance. They can provide expert guidance and help resolve complex issues.
21. Using Third-Party Tools
There are third-party tools available that can help force close unresponsive programs, including Excel. These tools often provide additional features and options to manage and control running processes.
22. Closing Excel from the Command Line
For advanced users, closing Excel from the command line can be an option. This method involves using specific commands to terminate the Excel process. However, it requires caution and a good understanding of the command-line interface.
23. Managing Excel’s Memory Usage
Excel can consume a significant amount of memory, especially when working with large datasets. Managing its memory usage can prevent it from becoming unresponsive. You can adjust Excel’s memory settings or close other memory-intensive programs to free up resources.
24. Checking for Hardware Issues
Sometimes, hardware-related issues can cause Excel to freeze or become unresponsive. Check your computer’s hardware, such as RAM, hard drive, or graphics card, for any potential problems. Upgrading or replacing faulty hardware may resolve the issue.
25. Using Excel’s Built-in Help
Excel provides a comprehensive help system that can guide you through various issues. Access the help system by clicking on the Help tab or pressing F1. Search for keywords related to your problem, and Excel will provide relevant solutions and troubleshooting steps.
Conclusion
Forcing close Excel may be necessary when it becomes unresponsive or freezes. In this guide, we explored various methods to gracefully exit Excel, ensuring a smooth and efficient process. From using Task Manager and keyboard shortcuts to repairing installations and running Excel in Safe Mode, these techniques can help you regain control over your computer. Remember to save your work frequently and consider creating backups to avoid data loss. With these tools at your disposal, you can navigate Excel-related issues with ease and confidence.
Can I recover unsaved work in Excel after a forced close?

+
Yes, Excel has a built-in recovery mode that can help recover unsaved work. Open Excel and go to the File tab, then select Open and navigate to the Recover Unsaved Workbooks folder. Locate the unsaved workbook and open it to recover your work.
Will forcing close Excel result in data loss?

+
Forcing close Excel may result in data loss if you have unsaved work. It is always recommended to save your work frequently to minimize the risk of data loss. However, Excel’s recovery mode can help recover unsaved work in certain cases.
What if none of the methods work to force close Excel?

+
If none of the methods mentioned in this guide work, it is recommended to contact Microsoft Support for further assistance. They can provide expert guidance and help resolve complex issues related to Excel.
Can I prevent Excel from becoming unresponsive in the future?

+
While it is not always possible to prevent Excel from becoming unresponsive, regular maintenance and updates can help improve its stability. Keep your Excel installation up to date, clear temporary files, and manage memory usage to ensure a smoother experience.
Are there any alternative methods to force close Excel?
+
Yes, there are third-party tools available that can help force close unresponsive programs, including Excel. These tools often provide additional features and options to manage and control running processes. However, it is always recommended to explore the methods mentioned in this guide first before considering third-party tools.