In the world of electrical engineering and electronics, the term "short circuit" is a concept that often arises and can have significant implications. A short circuit occurs when an unintended connection is made between two points of a circuit, typically resulting in excessive current flow and potentially damaging consequences. This phenomenon is not limited to electrical systems; it can also occur in other fields such as fluid dynamics and thermodynamics. Understanding the definition and implications of a short circuit is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems, as it can help prevent accidents, ensure safety, and maintain the integrity of the circuit.
Understanding the Short Circuit Phenomenon
A short circuit is a condition where there is a low-resistance path between two points in an electrical circuit that are meant to be at different voltages. This can happen due to various reasons, such as a faulty connection, damaged insulation, or the presence of a conductive material between the two points. When a short circuit occurs, the current flowing through the circuit increases significantly, often leading to overheating, component failure, and even fire hazards.
The excessive current flow during a short circuit can be attributed to the low resistance path created. In a normal circuit, the resistance limits the current flow to a safe level. However, when a short circuit occurs, the resistance drops dramatically, allowing a large amount of current to pass through. This sudden surge of current can cause the wires and components to heat up rapidly, potentially leading to their destruction.
Types of Short Circuits
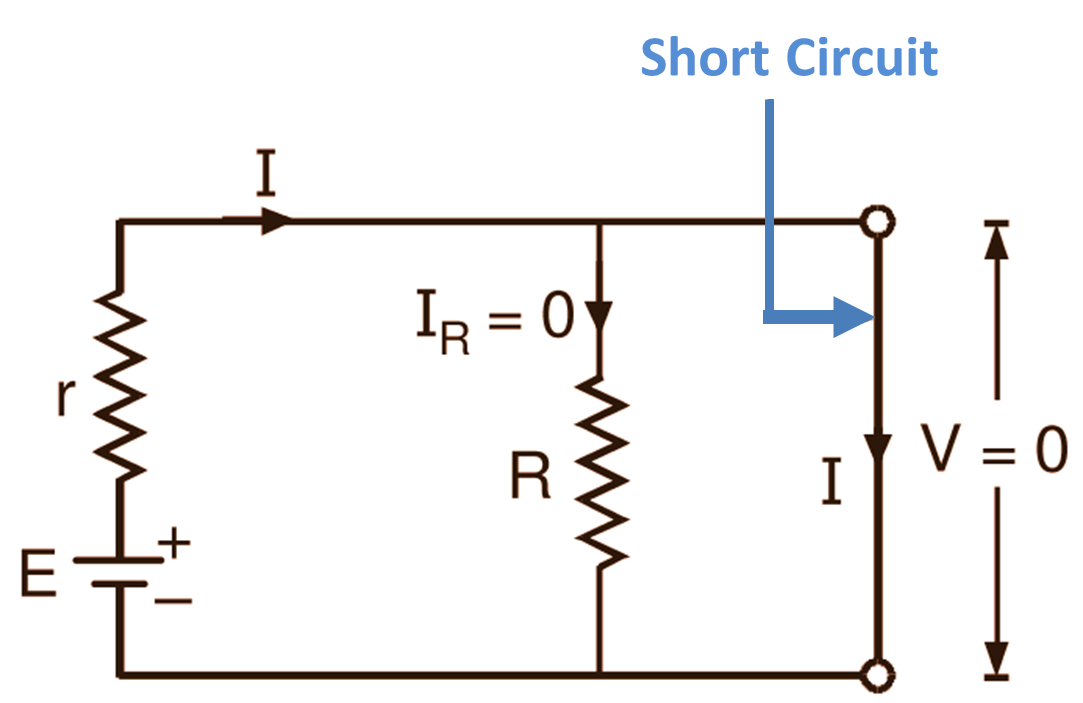
Short circuits can be classified into two main types: direct short circuits and indirect short circuits. Understanding the difference between these types is crucial for effective troubleshooting and prevention.
Direct Short Circuits
A direct short circuit occurs when there is a direct connection between two points in a circuit that are meant to have a potential difference. This type of short circuit is often caused by a physical fault, such as a damaged wire or a loose connection. The direct contact between the two points allows for a large current flow, bypassing the intended path of the circuit.
Indirect Short Circuits

An indirect short circuit, also known as a ground fault, occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a grounded conductor or a metallic object that is connected to the ground. This type of short circuit can be more subtle and harder to detect, as it may not always result in a complete circuit breakdown. However, indirect short circuits can still cause damage to equipment and pose safety risks.
Causes of Short Circuits
Short circuits can be caused by a variety of factors, and identifying the root cause is essential for effective prevention. Some common causes of short circuits include:
- Faulty wiring or damaged insulation
- Overloaded circuits or excessive current draw
- Corrosion or moisture damage to electrical components
- Improperly installed or damaged electrical equipment
- Physical damage to wires or connections
It is important to regularly inspect and maintain electrical systems to prevent short circuits. This includes checking for signs of wear and tear, ensuring proper insulation, and following safety guidelines when working with electrical equipment.
Effects of Short Circuits

The impact of a short circuit can vary depending on the severity and duration of the event. Some common effects of short circuits include:
- Overheating of wires and components, leading to their damage or failure
- Tripping of circuit breakers or fuses, causing a power outage
- Damage to sensitive electronic devices, such as computers or smartphones
- Fire hazards due to the excessive heat generated
- Electrical shocks or hazards, especially in the case of indirect short circuits
It is crucial to address short circuits promptly to minimize the potential damage and ensure the safety of individuals and equipment. Proper circuit protection, such as circuit breakers and fuses, can help prevent catastrophic failures and provide a level of safety against short circuits.
Preventing Short Circuits

Preventing short circuits is essential for the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. Here are some key strategies to minimize the risk of short circuits:
- Regular maintenance and inspection of electrical systems
- Proper installation and use of high-quality electrical components
- Avoiding overloading circuits and managing power consumption
- Implementing proper grounding and earthing systems
- Using circuit protection devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses
By following these preventive measures, the likelihood of short circuits can be significantly reduced. It is also important to educate individuals working with electrical systems about the potential dangers and the proper safety protocols to follow.
Conclusion and Safety Considerations
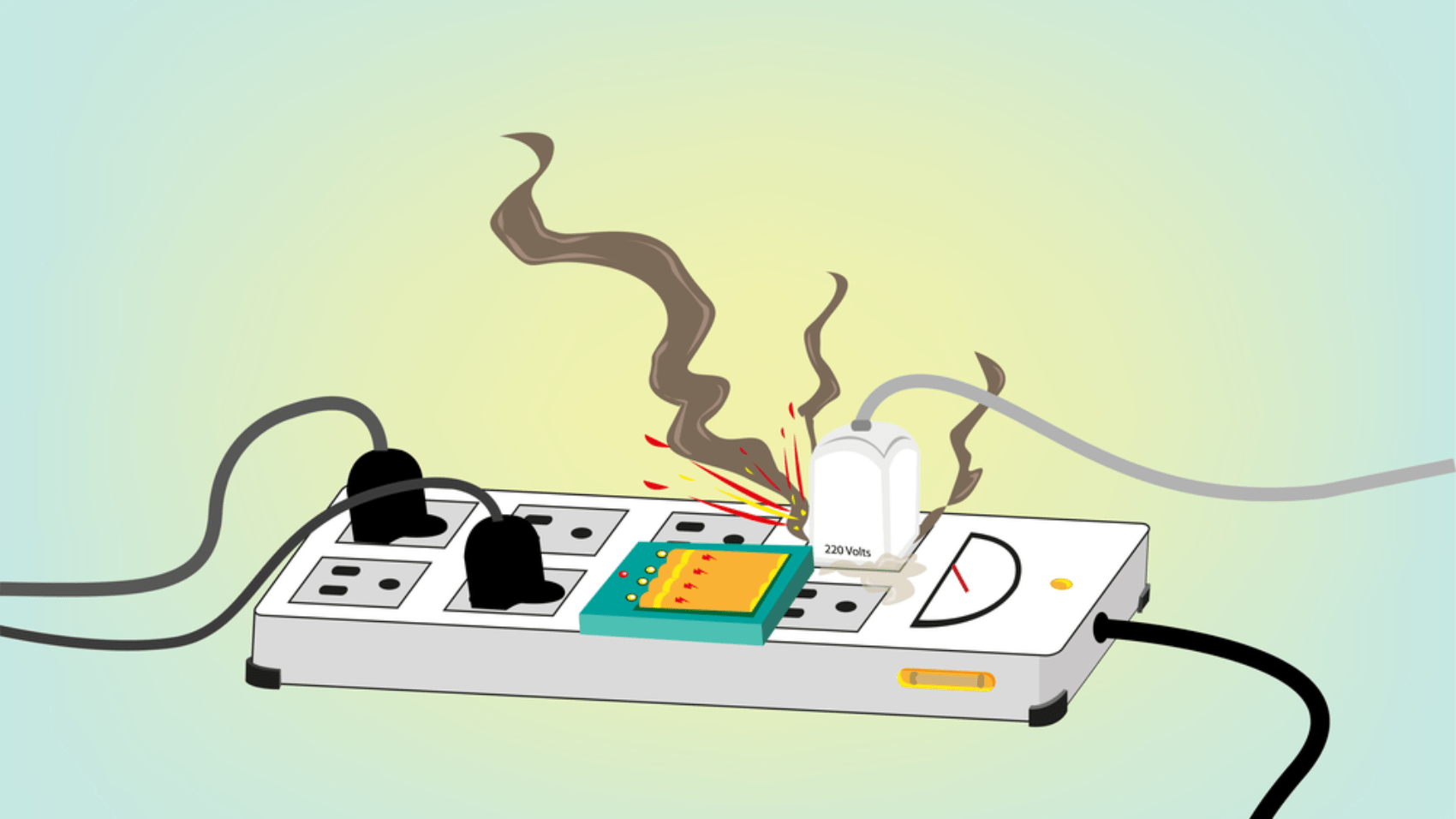
In conclusion, a short circuit is a serious electrical phenomenon that can have detrimental effects on equipment and pose safety hazards. Understanding the definition, types, causes, and effects of short circuits is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. By implementing preventive measures and promoting safety awareness, the risk of short circuits can be minimized, ensuring the reliable and safe operation of electrical circuits.
Common Questions and Answers

What is the main cause of short circuits?
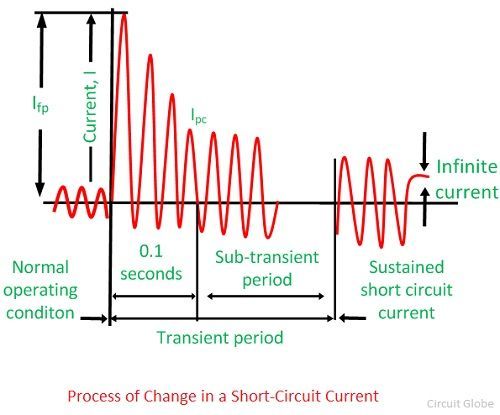
+
Short circuits are primarily caused by faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or the presence of conductive materials between two points in a circuit. These factors can lead to a low-resistance path, allowing excessive current flow.
How can I prevent short circuits in my home electrical system?
+
To prevent short circuits, ensure regular maintenance and inspection of your electrical system. Use high-quality components, avoid overloading circuits, and implement proper grounding. Additionally, educate yourself and your family about electrical safety practices.
What are the signs of a potential short circuit?

+
Signs of a potential short circuit include flickering lights, burning smells, unusual sounds from electrical equipment, or frequent tripping of circuit breakers. If you notice any of these signs, it is important to investigate and address the issue promptly.
Can short circuits be fixed, or do they require replacement?

+
The repair or replacement of components affected by a short circuit depends on the severity of the damage. In some cases, simple repairs and maintenance can resolve the issue. However, if the damage is extensive, it may require the replacement of affected components or even the entire circuit.
Are short circuits always visible or detectable?

+
Short circuits can sometimes be subtle and not easily detectable. Indirect short circuits, in particular, may not always result in a complete circuit breakdown. Regular maintenance and the use of circuit protection devices can help identify and prevent potential short circuits.