Understanding the derivative of arcsin is a fundamental concept in calculus, providing insights into the rate of change of inverse trigonometric functions. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the derivative of arcsin, offering a comprehensive guide to its process and applications.
The Derivative of Arcsin
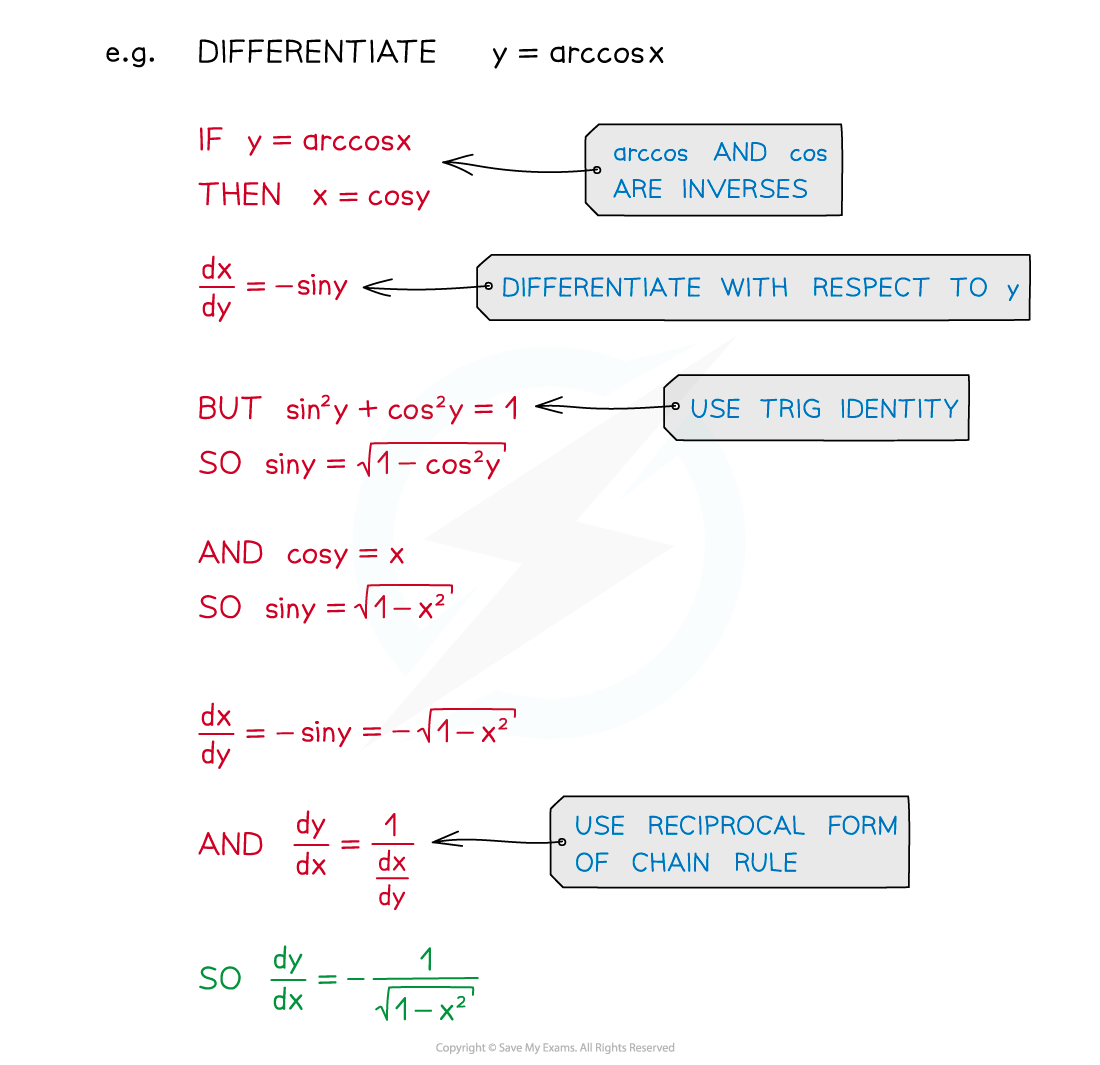
The derivative of the arcsin function, often denoted as arcsin(x) or sin-1(x), is a mathematical concept that represents the rate of change of the arcsin function with respect to its input variable x. In simpler terms, it tells us how the output of the arcsin function changes as the input x varies.
The derivative of arcsin(x) is given by the formula:
arcsin(x)′ = 1 / √(1 - x2)
This formula provides a concise representation of the rate of change of the arcsin function. It is important to note that the derivative of arcsin(x) is not a simple function, but rather a reciprocal of a square root function. This complexity arises from the inverse trigonometric nature of the arcsin function.
Derivation Process

Deriving the formula for the derivative of arcsin(x) involves a series of mathematical steps. Let's explore this process step-by-step:
- Start with the definition of arcsin(x):
arcsin(x) = y where sin(y) = x, and 0 ≤ y ≤ π
- Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to x:
cos(y) * y′ = 1
- Isolate y′ by dividing both sides by cos(y):
y′ = 1 / cos(y)
- Substitute x for sin(y) and simplify:
y′ = 1 / √(1 - sin2(y))
= 1 / √(1 - x2)
This derivation leads us to the formula for the derivative of arcsin(x), which is a key result in calculus.
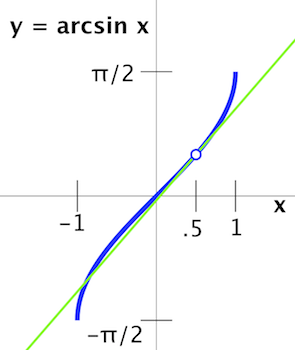
Graphical Interpretation

The derivative of arcsin(x) can be interpreted graphically as the slope of the tangent line to the graph of arcsin(x) at any point x. This slope represents the rate of change of the arcsin function at that particular point. As we move along the x-axis, the slope of the tangent line changes, indicating the varying rate of change of the function.
The graph of arcsin(x) is an increasing function within the range of -1 ≤ x ≤ 1, and its derivative reflects this behavior. The derivative is positive for 0 < x < 1, indicating that the function is increasing in this interval. Similarly, the derivative is negative for -1 < x < 0, indicating a decreasing function.
Applications of Arcsin Derivative

The derivative of arcsin(x) finds applications in various mathematical and scientific fields. Here are a few key applications:
- Physics: The derivative of arcsin(x) is used in the study of oscillatory motion, particularly in the analysis of simple harmonic oscillators.
- Engineering: It is applied in signal processing and control systems to analyze and design systems with inverse trigonometric functions.
- Statistics: The arcsin transformation is used in statistical analysis to stabilize variance in proportions and percentages.
- Mathematics: The derivative of arcsin(x) is a fundamental tool in calculus, helping to solve optimization problems and understand the behavior of inverse trigonometric functions.
Important Notes

💡 Note: When working with the derivative of arcsin(x), it's crucial to pay attention to the range of the function. The arcsin function is defined only for -1 ≤ x ≤ 1, so the derivative is valid within this range.
⚠️ Caution: The derivative of arcsin(x) is undefined at x = -1 and x = 1 due to the presence of a square root in the denominator. These points are known as vertical asymptotes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the derivative of arcsin(x) is a vital concept in calculus, providing insights into the rate of change of inverse trigonometric functions. Its formula, 1 / √(1 - x2), is a result of a rigorous derivation process. The derivative has practical applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, statistics, and mathematics. Understanding the derivative of arcsin(x) deepens our understanding of calculus and its applications in real-world scenarios.
What is the range of the arcsin function?
+
The range of the arcsin function is -π/2 ≤ y ≤ π/2, where y is the output of the function.
How is the derivative of arcsin(x) related to the derivative of sin(x)?
+
The derivative of arcsin(x) is the inverse of the derivative of sin(x). This relationship arises from the definition of inverse functions.
Can the derivative of arcsin(x) be negative?

+
Yes, the derivative of arcsin(x) can be negative for -1 < x < 0. This indicates that the function is decreasing in this interval.