Understanding molecular polarity is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and it plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes. One molecule that often sparks curiosity is CO2, or carbon dioxide. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of molecular polarity and answer the question: Is CO2 polar? By exploring the electronic configuration, molecular geometry, and bond types of CO2, we will gain a deeper understanding of its polarity status.
The Electronic Configuration of CO2

To determine the polarity of a molecule, we must first examine its electronic configuration. CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a molecule composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The carbon atom has four valence electrons, while each oxygen atom contributes six valence electrons. In CO2, the carbon atom forms double bonds with both oxygen atoms, resulting in a total of four bonding electrons.
The electronic configuration of CO2 can be represented as follows:
Carbon (C): 1s2 2s2 2p2 Oxygen (O): 1s2 2s2 2p4
In CO2, the carbon atom shares its four valence electrons with the oxygen atoms to form double bonds. This sharing of electrons results in a stable molecular structure.
Molecular Geometry and Bond Types

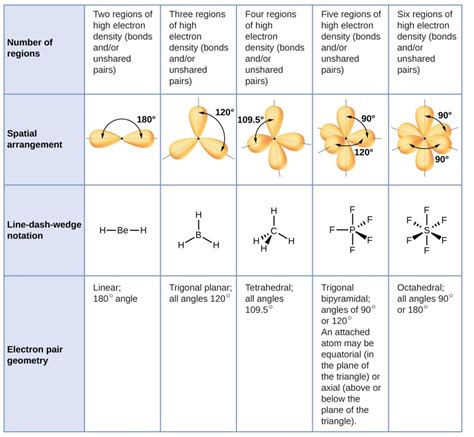
The molecular geometry of CO2 is linear, with the carbon atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms on either side. This linear geometry is a result of the double bonds between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The bond angles in CO2 are approximately 180 degrees, creating a symmetrical structure.
The bond types in CO2 are primarily covalent bonds. Covalent bonds occur when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. In CO2, the carbon-oxygen double bonds are covalent, as the carbon atom shares its electrons with the oxygen atoms to form a stable molecule.
Understanding Molecular Polarity

Molecular polarity refers to the distribution of electrons within a molecule, which can result in the formation of electric dipoles. An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule, creating a polar molecule. The polarity of a molecule is influenced by several factors, including the electronegativity difference between the atoms and the molecular geometry.
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Atoms with higher electronegativity have a stronger attraction for electrons, while atoms with lower electronegativity have a weaker attraction. When two atoms with different electronegativities form a bond, the electrons are not shared equally, leading to the formation of a polar bond.
Is CO2 Polar or Non-Polar?
Now, let's address the main question: Is CO2 polar? To determine the polarity of CO2, we need to consider the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen atoms and the molecular geometry.
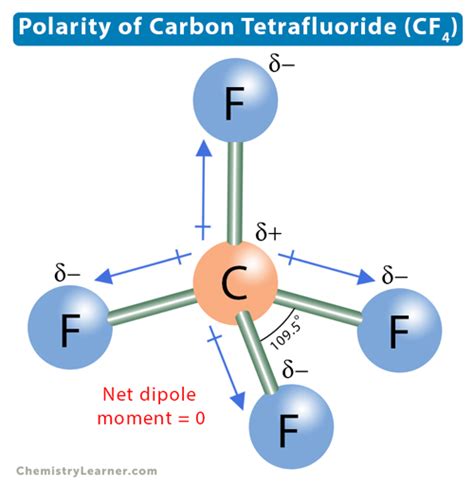
Carbon and oxygen atoms have significantly different electronegativity values. Oxygen, with an electronegativity of 3.44, is much more electronegative than carbon, which has an electronegativity of 2.55. This electronegativity difference leads to an unequal sharing of electrons in the carbon-oxygen bonds.
In CO2, the carbon atom is bonded to two highly electronegative oxygen atoms. As a result, the electrons in the carbon-oxygen bonds are pulled towards the oxygen atoms, creating a partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom. This charge separation creates an electric dipole moment, making CO2 a polar molecule.
The linear molecular geometry of CO2 also contributes to its polarity. The symmetrical arrangement of the oxygen atoms around the carbon atom ensures that the partial charges are evenly distributed, resulting in a balanced dipole moment.
Polar vs. Non-Polar Molecules

Understanding the difference between polar and non-polar molecules is essential in chemistry. Polar molecules, like CO2, have an uneven distribution of electrons, leading to the formation of electric dipoles. This polarity can have significant implications in various chemical and physical properties, such as solubility, boiling point, and reactivity.
Non-polar molecules, on the other hand, have an equal distribution of electrons, resulting in a symmetrical electron cloud. This symmetry ensures that there is no separation of charges, making non-polar molecules electrically neutral.
Examples of Polar and Non-Polar Molecules

To further illustrate the concept of molecular polarity, let's explore some examples of polar and non-polar molecules.
Polar Molecules

- Water (H2O): Water is a classic example of a polar molecule. The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms, leading to an uneven distribution of electrons and the formation of a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom.
- Ammonia (NH3): Ammonia is another polar molecule. The nitrogen atom, being more electronegative than hydrogen, pulls the electrons towards itself, creating a partial negative charge on the nitrogen atom.
Non-Polar Molecules

- Methane (CH4): Methane is a non-polar molecule. The carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms, and the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is minimal. This results in an equal sharing of electrons and a symmetrical electron cloud.
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen gas, consisting of two oxygen atoms, is non-polar. The electronegativity difference between the oxygen atoms is negligible, leading to an equal distribution of electrons and a non-polar molecule.
The Impact of Molecular Polarity
Molecular polarity has several significant implications in various scientific fields.
Solubility

Polar molecules tend to be more soluble in polar solvents, while non-polar molecules are more soluble in non-polar solvents. This concept is based on the "like dissolves like" principle, where molecules with similar polarity interact and dissolve more readily.
Boiling and Melting Points

Polar molecules generally have higher boiling and melting points compared to non-polar molecules. This is because polar molecules have stronger intermolecular forces, such as dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding, which require more energy to break.
Reactivity

Molecular polarity can influence the reactivity of a molecule. Polar molecules often exhibit different chemical behaviors and react differently with other molecules compared to non-polar molecules. This is due to the presence of electric dipoles and the resulting intermolecular interactions.
Practical Applications of Molecular Polarity

Understanding molecular polarity has numerous practical applications in various industries.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, molecular polarity plays a crucial role in drug design and development. The polarity of a drug molecule can affect its solubility, absorption, and distribution within the body. By manipulating the polarity, scientists can optimize drug efficacy and minimize side effects.
Environmental Science

Molecular polarity is essential in environmental science, particularly in understanding the behavior of pollutants and their impact on the environment. The polarity of a pollutant molecule can determine its solubility in water, its ability to interact with other molecules, and its potential to bioaccumulate in living organisms.
Materials Science

In materials science, molecular polarity is crucial for developing new materials with specific properties. By controlling the polarity of molecules, scientists can create materials with desired characteristics, such as conductivity, flexibility, or adhesion.
Conclusion

In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the concept of molecular polarity and answered the question: Is CO2 polar? We have learned that CO2 is indeed a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen atoms and the linear molecular geometry. Understanding molecular polarity is essential in various scientific fields, as it influences solubility, boiling points, reactivity, and practical applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and materials science.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is molecular polarity?

+
Molecular polarity refers to the distribution of electrons within a molecule, which can result in the formation of electric dipoles. It is influenced by factors such as electronegativity difference and molecular geometry.
How does electronegativity affect molecular polarity?
+
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. When atoms with different electronegativities form a bond, the electrons are not shared equally, leading to the formation of a polar bond.
What are the implications of molecular polarity?
+Molecular polarity can impact solubility, boiling and melting points, and reactivity. Polar molecules have specific interactions with other polar molecules, while non-polar molecules interact with non-polar substances.