Understanding Indiana’s Minimum Wage

Indiana’s minimum wage is a crucial aspect of the state’s labor laws, impacting the lives of countless workers and businesses alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Indiana’s minimum wage, exploring its history, current rates, and the factors influencing its determination. Whether you’re an employee, employer, or simply curious about labor rights, this blog will provide you with a deep understanding of this essential topic.
The Evolution of Indiana’s Minimum Wage
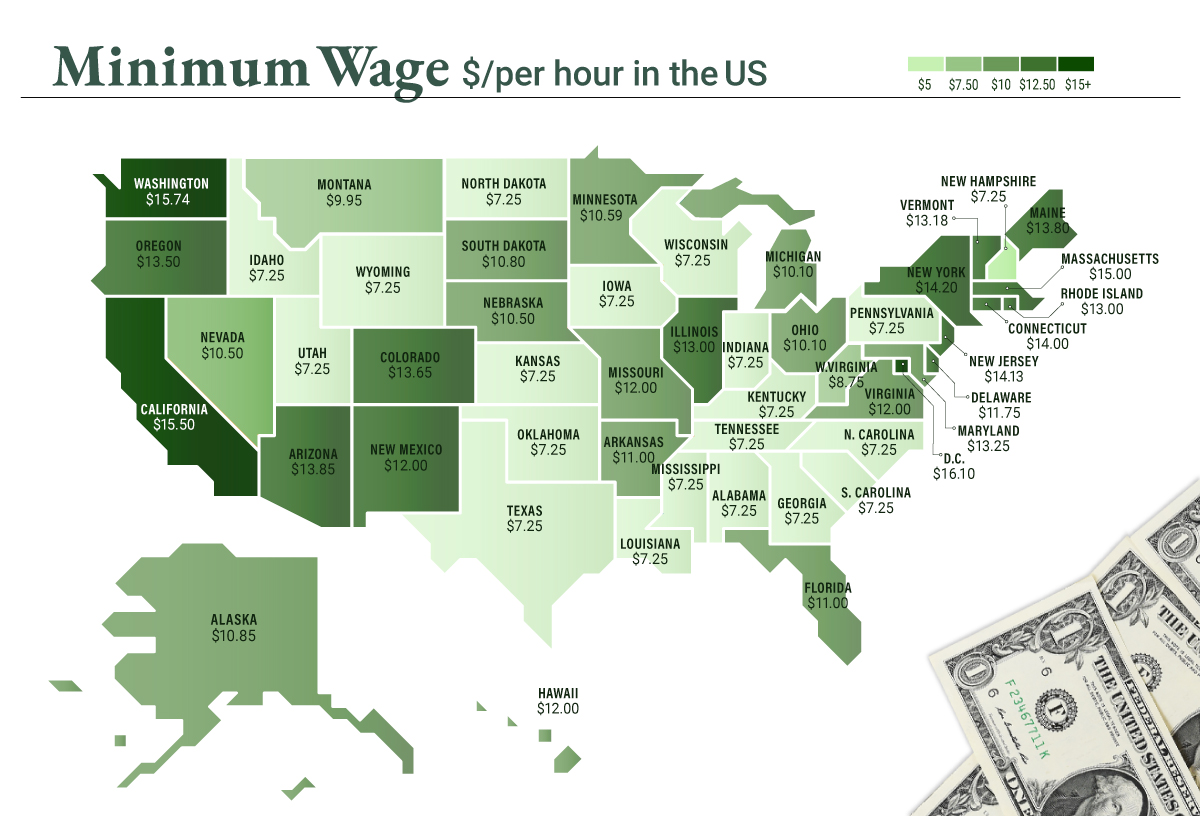
Indiana’s journey towards establishing a minimum wage began with the federal Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in 1938. This landmark legislation set the initial federal minimum wage at $0.25 per hour, aiming to ensure fair compensation for workers across the nation. Over the years, both the federal and state governments have played a role in shaping Indiana’s minimum wage, with periodic adjustments to keep pace with the changing economic landscape.
Current Minimum Wage Rates in Indiana

As of my last update in January 2023, Indiana’s minimum wage is set at $7.25 per hour, matching the federal minimum wage. This rate applies to most employees in the state, providing a baseline for fair compensation. However, it’s important to note that certain industries and occupations may have different minimum wage requirements, as we will explore further.
Exceptions and Variations
Indiana’s minimum wage is not a one-size-fits-all policy. Several exceptions and variations exist, catering to the diverse nature of the state’s workforce. Here are some key instances where different minimum wage rates may apply:
Tipped Employees: Workers who receive tips, such as servers and bartenders, are subject to a lower minimum wage rate. In Indiana, the minimum wage for tipped employees is $2.13 per hour, provided that their total earnings (including tips) meet or exceed the federal minimum wage.
Apprentices and Trainees: Individuals undergoing apprenticeship or training programs may be eligible for a lower minimum wage, as these programs often involve on-the-job training and skill development. The specific rate for apprentices and trainees can vary depending on the industry and the terms of the training agreement.
Students: Certain students, particularly those enrolled in vocational or educational programs, may be employed at a lower minimum wage rate. This exception is designed to provide work experience and skill development opportunities for students while allowing employers to offer more affordable labor.
Full-Time Students: Full-time students employed by colleges or universities may also be subject to a different minimum wage rate. These institutions often have specific policies and agreements in place to accommodate student workers, ensuring a balance between work and academic commitments.
Individuals with Disabilities: Indiana’s minimum wage laws also consider the unique circumstances of individuals with disabilities. In some cases, employers may be permitted to pay a subminimum wage to workers with disabilities, provided that it aligns with their productivity and abilities. This exception aims to provide employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities while recognizing their specific needs.
Factors Influencing Minimum Wage Rates
The determination of minimum wage rates in Indiana is a complex process influenced by various economic, social, and political factors. Here are some key considerations that play a role in setting and adjusting minimum wage rates:
Cost of Living: The cost of living in Indiana varies across different regions and communities. Minimum wage rates are often adjusted to reflect these variations, ensuring that workers can afford basic necessities such as housing, transportation, and utilities.
Inflation: Over time, the value of money can erode due to inflation. To maintain the purchasing power of workers, minimum wage rates are periodically reviewed and adjusted to account for inflationary trends.
Economic Conditions: The overall economic health of the state and the nation can impact minimum wage rates. During periods of economic growth and prosperity, minimum wage increases may be more feasible, while economic downturns may require a more cautious approach.
Political Landscape: Political factors, including public opinion and legislative priorities, can influence the determination of minimum wage rates. Political leaders and policymakers play a crucial role in shaping labor laws and advocating for fair compensation for workers.
Industry-Specific Considerations: Certain industries may have unique characteristics that warrant different minimum wage rates. For example, industries with high labor costs or specific skill requirements may face challenges in paying the standard minimum wage. In such cases, exceptions or variations may be implemented to ensure the viability of these industries while still providing fair compensation to workers.
Compliance and Enforcement

Ensuring compliance with minimum wage laws is a shared responsibility between employers and employees. Employers must accurately calculate and pay the appropriate minimum wage, while employees have the right to report any violations or discrepancies. Indiana’s Department of Labor plays a vital role in enforcing minimum wage laws, investigating complaints, and taking appropriate action against non-compliant employers.
The Impact on Workers and Businesses

Indiana’s minimum wage has a significant impact on both workers and businesses. For workers, a fair minimum wage ensures that they can meet their basic needs and maintain a decent standard of living. It empowers individuals to pursue their goals, invest in their education, and contribute to their communities. On the other hand, businesses must navigate the challenges of paying a higher minimum wage, including potential increases in labor costs and the need to adjust their business models to remain competitive.
Conclusion

Indiana’s minimum wage is a dynamic and evolving aspect of the state’s labor landscape. From its historical roots to the current rates and exceptions, understanding the intricacies of minimum wage laws is essential for both employees and employers. By staying informed and engaged, we can contribute to a fair and prosperous workforce, ensuring that Indiana’s workers receive the compensation they deserve while businesses thrive in a competitive economy.
FAQ

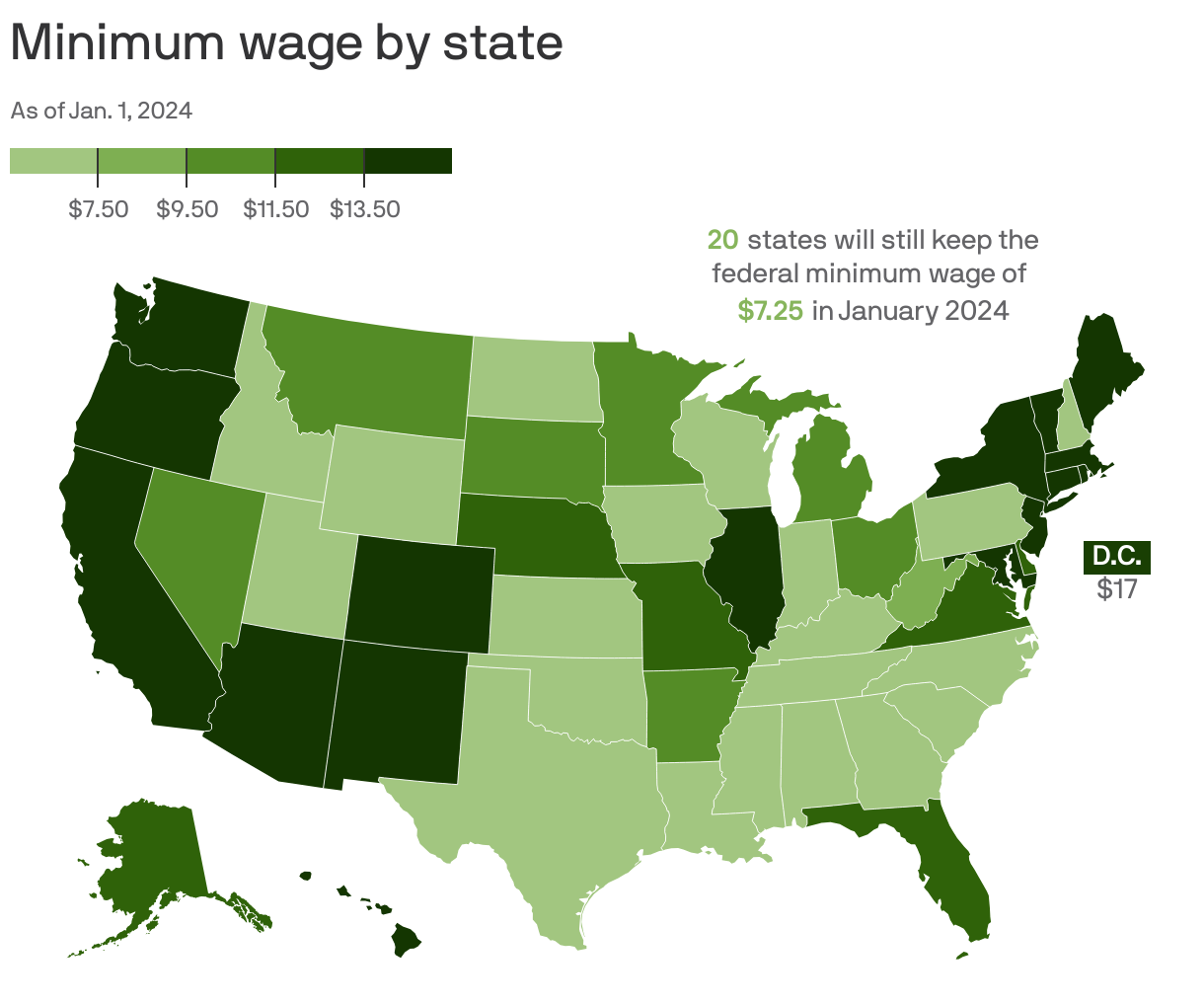
What is the current minimum wage in Indiana?
+
As of my last update in January 2023, Indiana’s minimum wage is $7.25 per hour, matching the federal minimum wage.
Are there any exceptions to Indiana’s minimum wage law?

+
Yes, Indiana’s minimum wage law includes exceptions for tipped employees, apprentices, trainees, students, and individuals with disabilities. These exceptions allow for variations in minimum wage rates based on specific circumstances.
How are minimum wage rates determined in Indiana?

+
Minimum wage rates in Indiana are influenced by factors such as the cost of living, inflation, economic conditions, political landscape, and industry-specific considerations. These factors are taken into account when setting and adjusting minimum wage rates to ensure fairness and viability.
What happens if an employer violates Indiana’s minimum wage law?
+Indiana’s Department of Labor is responsible for enforcing minimum wage laws. Employers who violate these laws may face penalties, including fines and legal action. Employees who believe their rights have been violated can file complaints with the Department of Labor for investigation and resolution.
How can I stay informed about changes to Indiana’s minimum wage?
+To stay updated on changes to Indiana’s minimum wage, you can regularly check the official website of the Indiana Department of Labor or subscribe to their newsletters and updates. Additionally, staying engaged with local news and labor organizations can provide valuable insights into any proposed changes or adjustments to minimum wage rates.