The Taylor expansion of the sine function, sin(x), is a powerful mathematical tool that allows us to approximate the value of the sine function for any real number x. It is an essential concept in calculus and has numerous applications in various fields. In this blog post, we will explore the Taylor expansion of sin(x), its derivation, and its significance.
Understanding the Taylor Expansion

The Taylor expansion, named after the English mathematician Brook Taylor, provides a way to represent a function as an infinite sum of terms. It allows us to approximate a function's value at a specific point by considering its derivatives at that point. The general form of the Taylor series for a function f(x) centered at a point a is given by:
f(x) = f(a) + f'(a)(x - a) + f''(a)(x - a)^2/2! + f'''(a)(x - a)^3/3! + ...
Here, f'(a) represents the first derivative of f(x) evaluated at a, f''(a) represents the second derivative, and so on. The factorials (!) in the denominator are included to account for the rate of change of higher-order derivatives.
Deriving the Taylor Expansion of sin(x)

To derive the Taylor expansion of sin(x), we need to find the derivatives of the sine function and evaluate them at a specific point, usually at x = 0. Let's start by recalling the definition of the sine function:
sin(x) = y where y is the y-coordinate of a point on the unit circle with an angle of x radians.
Now, let's find the derivatives of sin(x):
- First derivative:
sin'(x) = cos(x) - Second derivative:
sin''(x) = -sin(x) - Third derivative:
sin'''(x) = -cos(x) - And so on, with the derivatives repeating in a cyclic pattern.
Next, we evaluate these derivatives at x = 0:
- sin(0) = 0
- cos(0) = 1
- sin'(0) = cos(0) = 1
- sin''(0) = -sin(0) = 0
- sin'''(0) = -cos(0) = -1
- And so on...
Now, we can substitute these values into the general Taylor series formula:
sin(x) = 0 + 1(x - 0) + 0(x - 0)^2/2! + (-1)(x - 0)^3/3! + ...
Simplifying the equation, we get:
sin(x) = x - x^3/3! + x^5/5! - x^7/7! + ...
This is the Taylor expansion of sin(x) centered at x = 0. The expansion consists of an infinite series of terms, each involving a power of x and a factorial in the denominator.
Significance and Applications
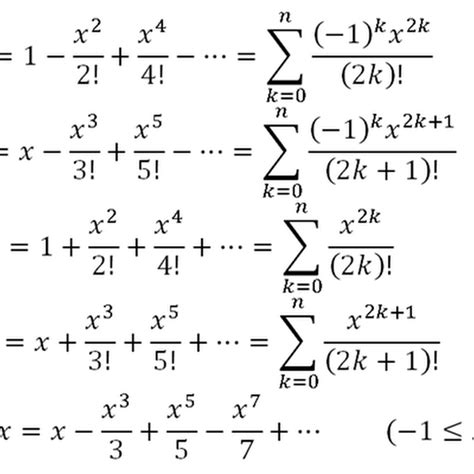
The Taylor expansion of sin(x) has wide-ranging applications in mathematics and various scientific fields. Here are some key points to consider:
- Approximation: The Taylor expansion provides an accurate approximation of the sine function for small values of x. As x increases, the error between the actual value of sin(x) and its Taylor approximation becomes more significant.
- Analytical Methods: The Taylor expansion is valuable for solving differential equations and analyzing the behavior of functions. It allows mathematicians and scientists to simplify complex functions and perform calculations more efficiently.
- Numerical Methods: In numerical analysis, the Taylor expansion is used to develop numerical methods for solving problems involving functions. It forms the basis for techniques like Taylor series expansion and numerical integration.
- Trigonometry: The Taylor expansion of sin(x) is closely related to the Maclaurin series, which is a special case of the Taylor series centered at x = 0. The Maclaurin series provides a concise representation of trigonometric functions and is widely used in trigonometric calculations.
Visualizing the Taylor Expansion

To better understand the Taylor expansion of sin(x), let's visualize it using a graph. The graph below compares the actual sine function with its Taylor approximation for different values of x:

🌐 Note: The graph illustrates how the Taylor approximation becomes more accurate as x approaches zero. For larger values of x, the approximation deviates from the actual sine function.
Limitations and Considerations

While the Taylor expansion is a powerful tool, it's essential to be aware of its limitations:
- Convergence: The Taylor series may not converge for all values of x. The convergence depends on the function and the point of expansion. In some cases, the series may converge slowly or not at all, leading to inaccurate approximations.
- Error Analysis: It's crucial to analyze the error between the actual function and its Taylor approximation. The error can be estimated using techniques like the Lagrange form of the remainder, which provides an upper bound on the error.
- Alternatives: In certain situations, other approximation methods like the Maclaurin series or Fourier series may be more suitable. These methods offer different advantages and are used depending on the specific problem at hand.
Conclusion

The Taylor expansion of sin(x) is a fundamental concept in calculus, providing an infinite series representation of the sine function. It allows us to approximate the value of sin(x) for any real number x and has numerous applications in mathematics and science. By understanding the derivation and significance of the Taylor expansion, we can harness its power to solve complex problems and gain deeper insights into the behavior of functions.
What is the Taylor expansion used for?

+
The Taylor expansion is used to approximate the value of a function at a specific point by considering its derivatives. It has applications in calculus, numerical analysis, and solving differential equations.
How accurate is the Taylor approximation of sin(x)?
+
The Taylor approximation of sin(x) is most accurate for small values of x. As x increases, the error between the actual sine function and its Taylor approximation becomes more significant.
What is the Maclaurin series, and how is it related to the Taylor expansion?

+
The Maclaurin series is a special case of the Taylor series, where the expansion is centered at x = 0. It provides a concise representation of trigonometric functions and is widely used in trigonometric calculations.
Are there any limitations to the Taylor expansion?

+
Yes, the Taylor expansion may not converge for all values of x, and the accuracy of the approximation depends on the function and the point of expansion. It’s essential to analyze the error and consider alternative approximation methods in certain situations.