Introduction to CO2

Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a fundamental chemical compound that plays a crucial role in various natural processes and human activities. It is a colorless and odorless gas, often referred to as a greenhouse gas due to its significant impact on the Earth’s climate. Understanding the properties of CO2, including its polarity, is essential for comprehending its behavior and interactions with other substances. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of polarity and explore whether CO2 can be classified as a polar molecule.
Understanding Polarity

Polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charges within a molecule. It is determined by the arrangement of atoms and the nature of their chemical bonds. When atoms form chemical bonds, they share electrons, and this sharing can be unequal, leading to the development of partial positive and negative charges. Polar molecules are those that possess a permanent dipole moment, meaning they have a separation of positive and negative charges, resulting in a net electrical polarity.
CO2 Structure and Bonding
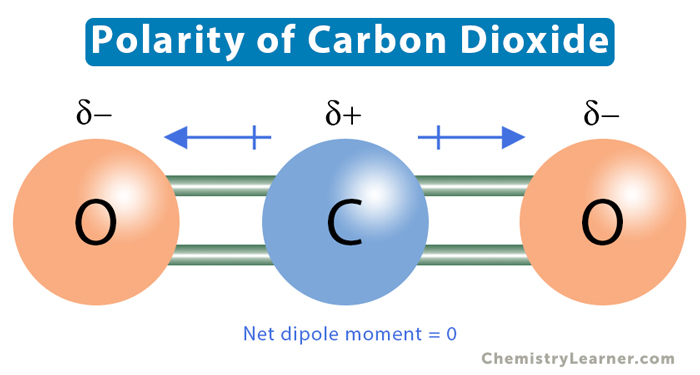
To determine if CO2 is polar, we must examine its molecular structure and bonding. CO2 consists of one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms. The carbon atom forms double bonds with both oxygen atoms, creating a linear structure. The double bonds, consisting of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond, are responsible for the unique properties of CO2.
Molecular Symmetry and Polarity
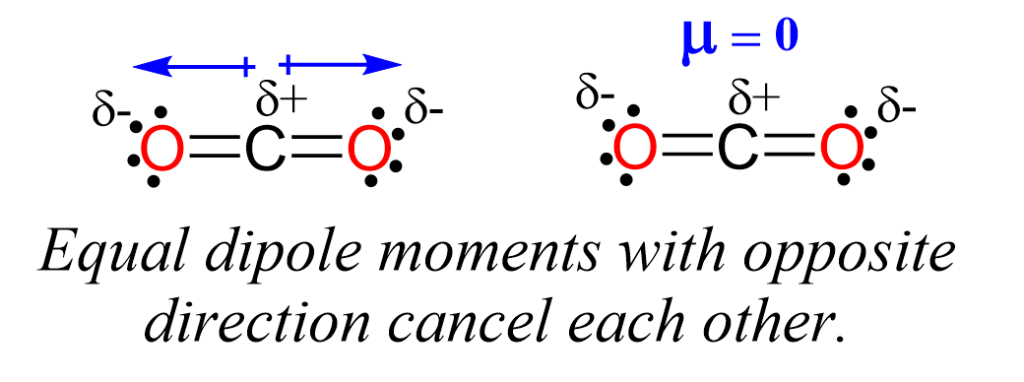
CO2 exhibits molecular symmetry, which is a crucial factor in determining its polarity. Symmetric molecules tend to have their charges evenly distributed, resulting in a zero net dipole moment. In the case of CO2, the linear structure ensures that the two oxygen atoms are positioned symmetrically on either side of the carbon atom. This symmetry cancels out any potential polarity that might arise from the difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen.
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity

Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself when bonded to another atom. In CO2, the carbon atom and the oxygen atoms have different electronegativity values. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, which means it has a stronger attraction for electrons. However, due to the symmetric arrangement of oxygen atoms, the electron density is evenly distributed, and the resulting bond polarity is canceled out.
Bond Dipole Moment

While CO2 does not possess a net dipole moment, it is essential to note that individual bonds within the molecule do exhibit some degree of polarity. The carbon-oxygen (C=O) double bonds have a bond dipole moment. A bond dipole moment occurs when one end of a bond is slightly more negative (oxygen) than the other end (carbon). However, in CO2, these bond dipoles cancel each other out due to the linear geometry of the molecule.
Comparison with Other Molecules

To further understand the polarity of CO2, let’s compare it with other molecules:
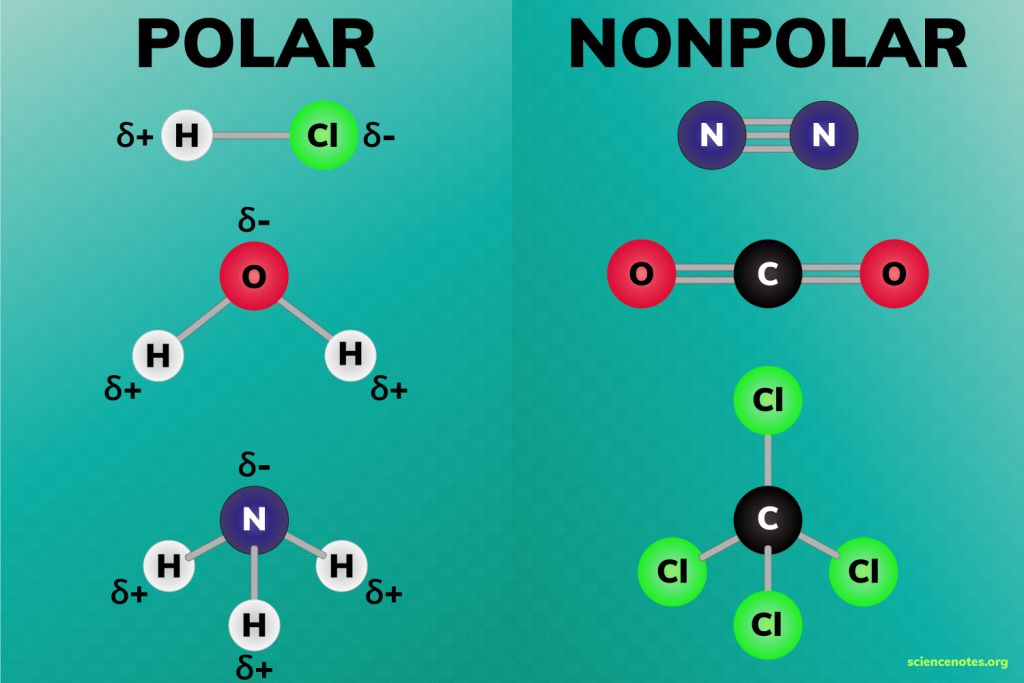
- Water (H2O): Water is a highly polar molecule due to its bent shape and the difference in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen. The oxygen atom attracts electrons more strongly, creating a negative pole, while the hydrogen atoms have a positive charge.
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen gas, consisting of two oxygen atoms, is non-polar. Although oxygen is highly electronegative, the equal sharing of electrons in the double bond results in a symmetric distribution of charge.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Carbon monoxide, like CO2, also has a linear structure. However, due to the difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen, CO is a polar molecule. The oxygen atom attracts electrons more strongly, leading to a net dipole moment.
Physical Properties and Polarity

The polarity of a molecule can influence its physical properties. Polar molecules tend to have higher boiling points and higher solubility in polar solvents. However, CO2, despite not being polar, exhibits some unique physical properties:
- Boiling Point: CO2 has a relatively low boiling point of -78.5°C. This is because it is a non-polar molecule, and the intermolecular forces between CO2 molecules are weaker compared to polar molecules.
- Solubility: CO2 is highly soluble in water, but this solubility is not solely due to polarity. The solubility of CO2 in water is attributed to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) and the resulting hydrogen bonding.
Applications and Impact

Understanding the polarity of CO2 has practical implications in various fields:
- Climate Change: CO2 is a significant greenhouse gas, and its polarity (or lack thereof) does not affect its ability to trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. The accumulation of CO2 contributes to global warming and climate change.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS technologies aim to capture and store CO2 emissions from industrial processes. The non-polar nature of CO2 plays a role in the selection of appropriate capture materials and storage methods.
- Agriculture: CO2 is essential for plant growth, as it is a key component in photosynthesis. The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere affects crop yields and agricultural practices.
Experimental Techniques to Determine Polarity
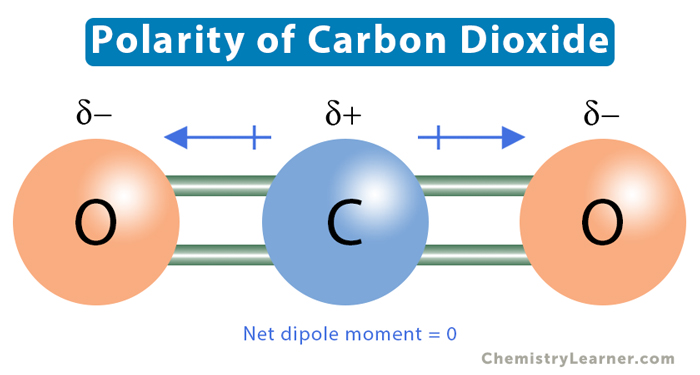
Scientists use various experimental techniques to determine the polarity of molecules:
- Spectroscopy: Techniques like infrared (IR) spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy can provide information about the vibrational and rotational modes of molecules, which are influenced by their polarity.
- Dielectric Constant: The dielectric constant measures a substance’s ability to reduce the electrical field between charged plates. Polar molecules have higher dielectric constants.
- X-ray Crystallography: This technique can determine the precise arrangement of atoms in a molecule, providing insights into its symmetry and polarity.
Conclusion: Is CO2 Polar?
In conclusion, carbon dioxide (CO2) is not considered a polar molecule. Its linear structure and symmetric arrangement of oxygen atoms result in a cancellation of any potential polarity that might arise from the difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen. The lack of a net dipole moment in CO2 sets it apart from highly polar molecules like water. However, the polarity of individual bonds within the molecule and its impact on physical properties are still areas of interest for further research and exploration.
FAQ
What is the difference between polar and non-polar molecules?

+
Polar molecules have a net dipole moment, meaning they possess a separation of positive and negative charges. Non-polar molecules, on the other hand, have their charges evenly distributed, resulting in a zero net dipole moment.
How does the polarity of a molecule affect its solubility in water?

+
Polar molecules tend to be more soluble in polar solvents like water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds and dipole-dipole interactions. Non-polar molecules, such as CO2, can still be soluble in water through other mechanisms, such as the formation of carbonic acid.
Can the polarity of a molecule change under different conditions?

+
Yes, the polarity of a molecule can be influenced by external factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of other substances. For example, increasing the temperature can enhance the mobility of molecules, potentially affecting their polarity.
What are some practical applications of understanding molecular polarity?
+
Understanding molecular polarity is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and materials science. It helps in designing drugs, optimizing chemical reactions, and developing new materials with specific properties. For instance, the polarity of a molecule can impact its interaction with biological membranes, making it an important consideration in drug delivery.
How can we determine the polarity of a molecule experimentally?

+
Scientists use various experimental techniques to determine molecular polarity, including spectroscopy (IR, Raman), dielectric constant measurements, and X-ray crystallography. These methods provide insights into the distribution of charges within a molecule.