Calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of change, both instantaneous and accumulative. It is a powerful tool that provides a deeper understanding of the behavior of various systems and processes in the world around us. Calculus forms the foundation for many scientific and engineering principles, making it an essential subject for students pursuing careers in these fields.
This blog post will delve into the core concepts of calculus, providing an in-depth exploration of its key principles and applications. By the end of this article, readers should have a solid grasp of the fundamentals of calculus and its importance in various scientific and mathematical contexts.
Understanding the Basics of Calculus

Calculus is primarily divided into two main branches: differential calculus and integral calculus. Differential calculus focuses on the study of rates of change and slopes of curves, while integral calculus deals with the accumulation of quantities and the calculation of areas under curves.
These two branches are interconnected and together form the foundation of calculus. Understanding both differential and integral calculus is crucial for solving complex problems and analyzing various real-world scenarios.
Differential Calculus

Differential calculus is concerned with the study of rates of change and how they relate to the slope of a curve. It provides a mathematical framework for understanding how small changes in one variable affect the rate of change of another variable. This concept is fundamental in physics, engineering, and economics, where the behavior of systems is often described in terms of rates of change.
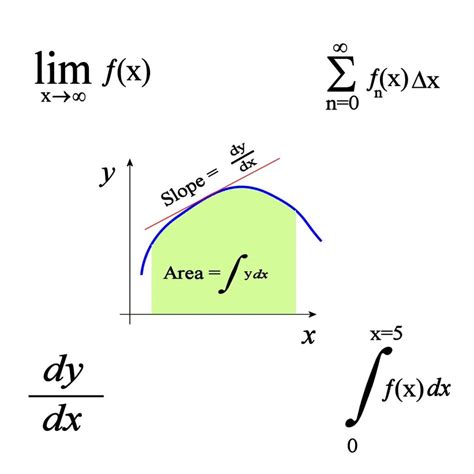
One of the key concepts in differential calculus is the derivative. The derivative of a function at a given point represents the rate of change of the function at that point. It provides information about the slope of the curve at that specific location. By calculating derivatives, we can analyze how quantities are changing with respect to each other, making it a powerful tool for understanding dynamic systems.
Some common applications of differential calculus include:
- Determining the velocity and acceleration of an object in motion.
- Analyzing the growth rate of populations or the decay rate of substances.
- Optimizing processes by finding the maximum or minimum values of functions.
- Modeling the behavior of systems in physics, such as the motion of planets or the flow of fluids.
Integral Calculus

Integral calculus, on the other hand, focuses on the accumulation of quantities and the calculation of areas under curves. It provides a way to determine the total amount of change that has occurred over a given interval. This concept is crucial in fields such as physics, where the calculation of work done or the determination of total displacement is essential.
The integral of a function represents the accumulation of the values of the function over a specific interval. It can be thought of as the inverse operation of differentiation. By integrating a function, we can find the total amount of change that has occurred, making it a powerful tool for solving problems involving accumulation.
Some common applications of integral calculus include:
- Calculating the area under a curve, which can represent the total distance traveled or the total amount of a substance produced.
- Determining the volume of a solid of revolution, such as a cylinder or a cone.
- Solving problems involving fluid flow, such as finding the total amount of fluid that has passed through a pipe.
- Modeling the accumulation of heat or the change in energy over time.
Techniques and Concepts in Calculus

Calculus is a vast subject, and there are numerous techniques and concepts that students need to master. Here are some of the key concepts and techniques that are essential for a solid understanding of calculus:
Limits and Continuity

Limits are a fundamental concept in calculus. They provide a way to understand the behavior of a function as it approaches a specific value. By studying limits, we can determine the rate of change of a function and its behavior at different points. Continuity, on the other hand, refers to the uninterrupted nature of a function. A continuous function has no breaks or jumps, making it easier to analyze and calculate derivatives and integrals.
Differentiation Rules
Differentiation rules are a set of formulas and techniques used to find the derivative of various functions. These rules include the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule. By applying these rules, we can differentiate a wide range of functions, making it easier to analyze their behavior and solve problems.
Integration Techniques

Integration techniques are methods used to find the integral of a function. There are several integration techniques, including integration by substitution, integration by parts, and trigonometric substitution. These techniques allow us to solve a wide variety of integration problems, making it possible to calculate areas, volumes, and other quantities.
Applications of Calculus

Calculus has numerous applications in various fields. Some of the key applications include:
- Physics: Calculus is used to model the motion of objects, the behavior of forces, and the propagation of waves.
- Engineering: It is essential for analyzing the behavior of structures, designing control systems, and optimizing processes.
- Economics: Calculus is used to model supply and demand, optimize production, and analyze consumer behavior.
- Computer Science: Calculus is fundamental in areas such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and graphics rendering.
- Statistics: Calculus is used in statistical analysis, especially in calculating probabilities and expectations.
Examples and Practice Problems

Practicing calculus problems is essential for developing a strong understanding of the subject. Here are a few examples to illustrate the concepts discussed earlier:
Differentiation Example

Find the derivative of the function f(x) = 3x2 - 2x + 1.
Solution:
To find the derivative, we can use the power rule, which states that the derivative of xn is n * xn-1. Applying this rule, we get:
f'(x) = 6x - 2
Integration Example

Calculate the integral of the function f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x + 3 with respect to x.
Solution:
To find the integral, we can use the power rule for integration, which states that the integral of xn is xn+1 / (n + 1). Applying this rule, we get:
F(x) = x4 / 4 + 2x3 / 3 - 5x2 / 2 + 3x + C
Application Example

A car is traveling at a velocity of v(t) = 2t - 3 meters per second, where t is time in seconds. Calculate the distance traveled by the car after 5 seconds.
Solution:
To find the distance traveled, we need to integrate the velocity function. The distance traveled is given by the integral of the velocity function with respect to time. So, we have:
d(t) = ∫ (2t - 3) dt
Integrating the function, we get:
d(t) = t2 - 3t + C
To find the distance traveled after 5 seconds, we plug in t = 5 into the equation:
d(5) = (52) - 3(5) + C
d(5) = 25 - 15 + C
Since we are interested in the distance traveled, the constant of integration C is zero. So, the distance traveled after 5 seconds is:
d(5) = 10 meters
Conclusion

Calculus is a powerful mathematical tool that allows us to understand and analyze the behavior of various systems and processes. By studying calculus, we gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and can solve complex problems in diverse fields. Whether it's optimizing processes, modeling physical phenomena, or analyzing data, calculus plays a vital role in our modern world.
By mastering the concepts and techniques of calculus, students can unlock a wide range of career opportunities in science, engineering, economics, and beyond. Calculus provides a solid foundation for further exploration and innovation, making it an essential subject for anyone interested in pursuing a career in these fields.
What are the key differences between differential and integral calculus?

+
Differential calculus focuses on rates of change and slopes of curves, while integral calculus deals with accumulation and areas under curves. Differential calculus is used to find derivatives, which represent rates of change, while integral calculus is used to find integrals, which represent accumulations.
How is calculus used in real-world applications?
+Calculus has numerous real-world applications, including modeling motion in physics, optimizing processes in engineering, analyzing financial data in economics, and improving machine learning algorithms in computer science.
What are some common challenges students face when learning calculus?
+Common challenges include understanding the concept of limits, mastering differentiation and integration techniques, and applying calculus to solve complex problems. It’s important to practice regularly and seek help when needed.
Are there any resources available for further learning and practice in calculus?
+Yes, there are numerous online resources, textbooks, and practice problems available. Websites like Khan Academy, WolframAlpha, and PatrickJMT offer comprehensive calculus tutorials and practice exercises. Additionally, seeking help from teachers or peers can greatly enhance your understanding.